
Epidemiological and mutational analysis of SARS-CoV-2
RECOVER-COVID19
RicErCa e sviluppO VERsus COVID19 in Campania
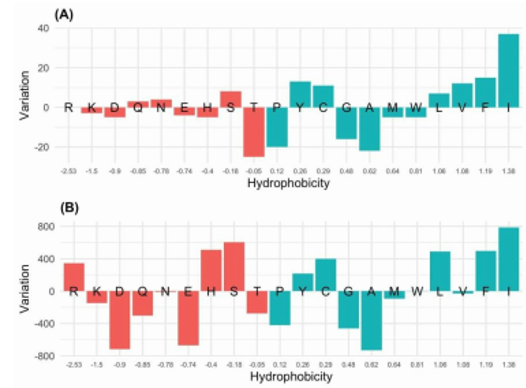
SARS-CoV-2 evolution: variation of amino acid composition
Track #1 (March 2020)
Number of deposited genomes 581
Number of mutations 404
Track #2 (October 2020)
Number of deposited genomes 135.404
Number of mutations 25.634
Track #3 (February 2021)
Number of deposited genomes 415,516
Number of mutations xxx
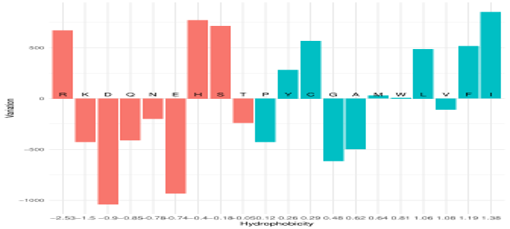
The estimation for each AA of its enrichment/depletion in counts of mutated versus original residues highlighted a trend of enrichment of hydrophobic residues and depletion of the hydrophilic ones. Among hydrophilic residues the arginine (R) is an exception being significantly enriched. This may be ascribed to the complicated hydrophobic/hydrophilic behavior of this residue that presents both a charged group (guanidinium) and an aliphatic chain extending from the Cα to the Cδ atoms.
SARS-CoV-2 evolution: hydrophobicity variation
Track #1 (March 2020)
Number of deposited genomes 581
Number of mutations 404
Track #2 (October 2020)
Number of deposited genomes 135.404
Number of mutations 25.634
Track #3 (February 2021)
Number of deposited genomes 415,516
Number of mutations xxx
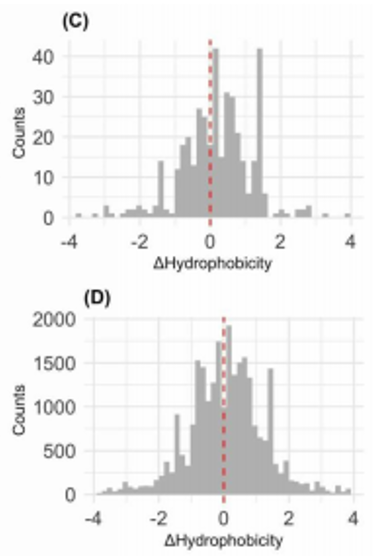
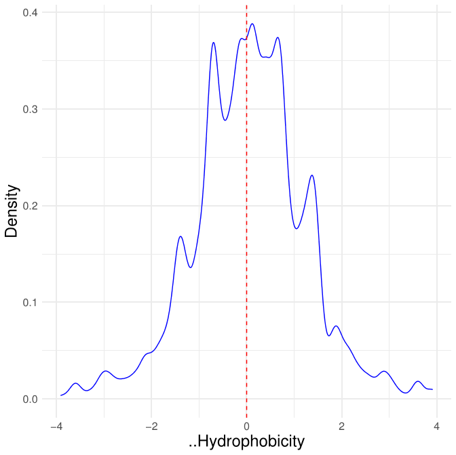
The differences in hydrophobicity (ΔHydrophobicity) between mutated and original residues averaged over all the observed mutations is slightly positive:
Track #1 0.18 ± 1.04
Track #2 0.08 ± 1.16
Track #3 XXXX