
Epidemiological and mutational analysis of SARS-CoV-2
RECOVER-COVID19
RicErCa e sviluppO VERsus COVID19 in Campania
SARS-CoV-2 adaptation to humans: frequency of aminoacid mutations
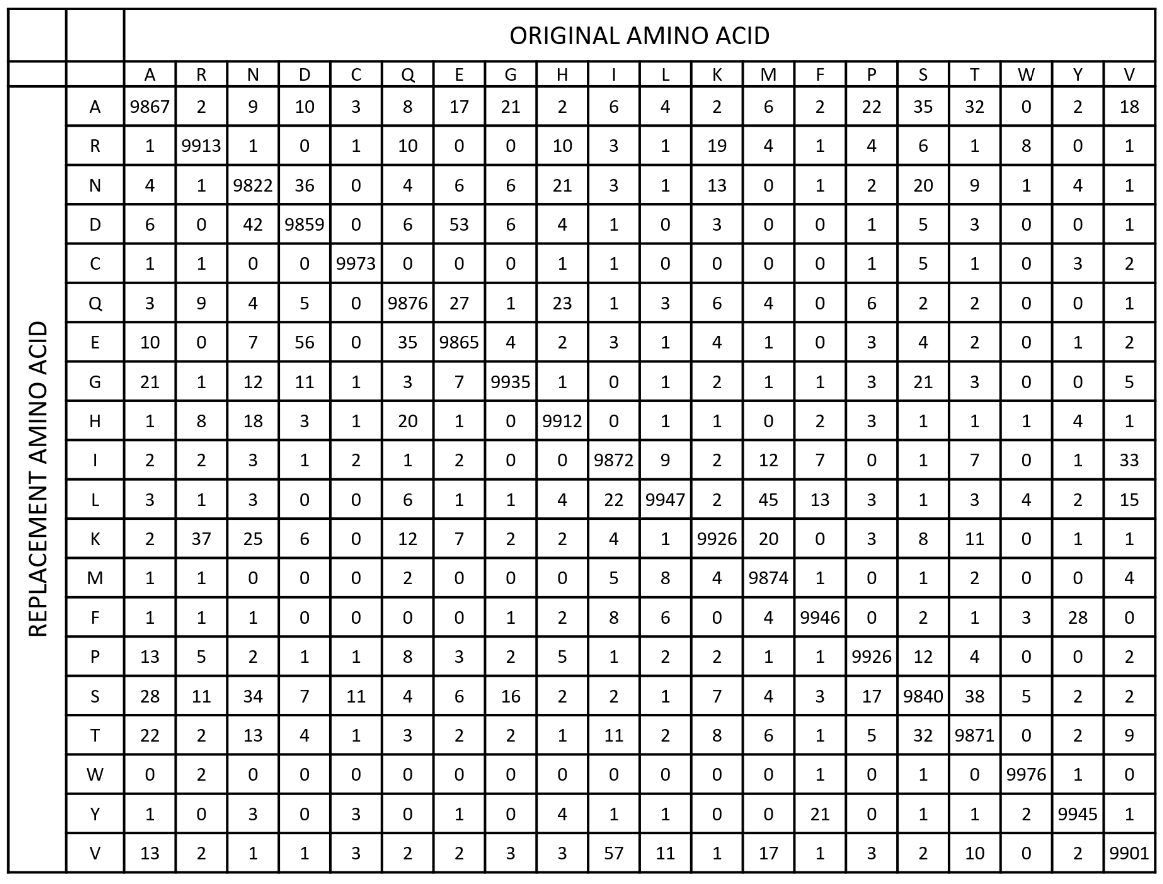
List of PAM values associated to all the 380 possible amino acid substitution types. The PAM value corresponds to the probability (multiplied by 10,000) that a certain amino acid (original AA) will be replaced by another amino acid (replacement AA) after a certain evolutionary interval (1 accepted point mutation per 100 amino acids).
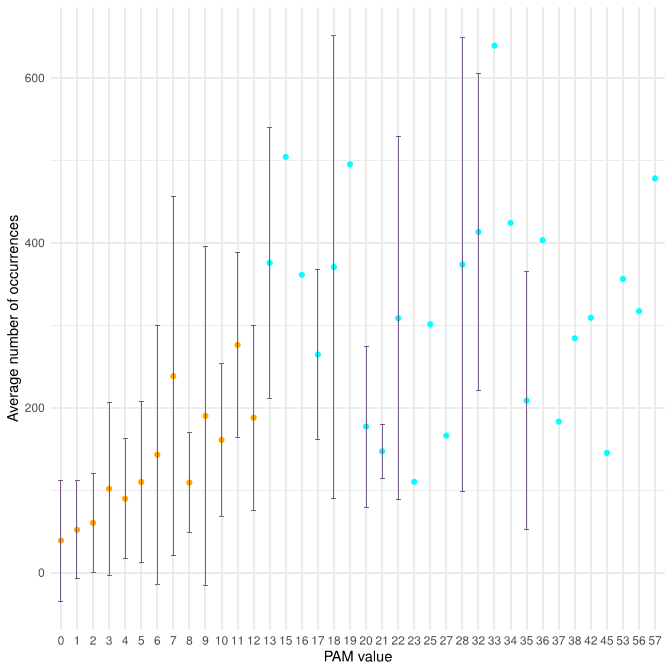
Frequency of aminoacid mutations
All mutations having PAM values larger than 12 can occur with a single base substitution. The PAM range of the substitutions requiring more than one change is 0-12.
| Theoretical | Pam 0-12 | Pam > 12 | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 base change | 107 | 43 | 150 |
| > 1 base change | 43 | - | 43 |
| Overall | 150 | 230 | 380 |
Based on the fact that high PAM values are associated with changes between AAs that present minimal differences in their chemico-physical properties, and based on the evidence that the maximum PAM value in substitutions that require more than one base change is 12, we define as non-conservative and conservative the mutations with PAM values falling in the range 0-12 and >12, respectively.
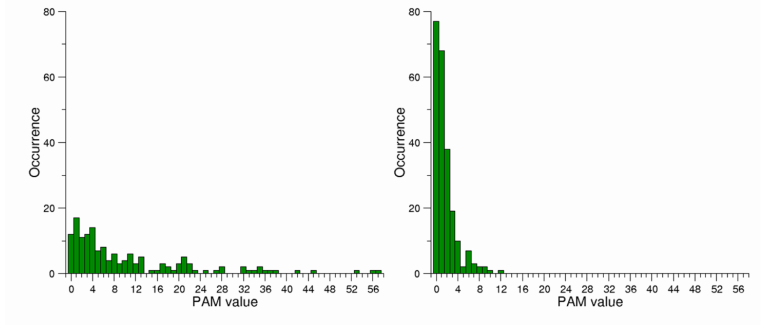
Number of mutations 404
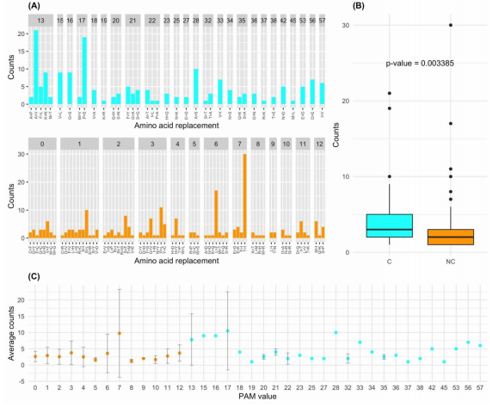
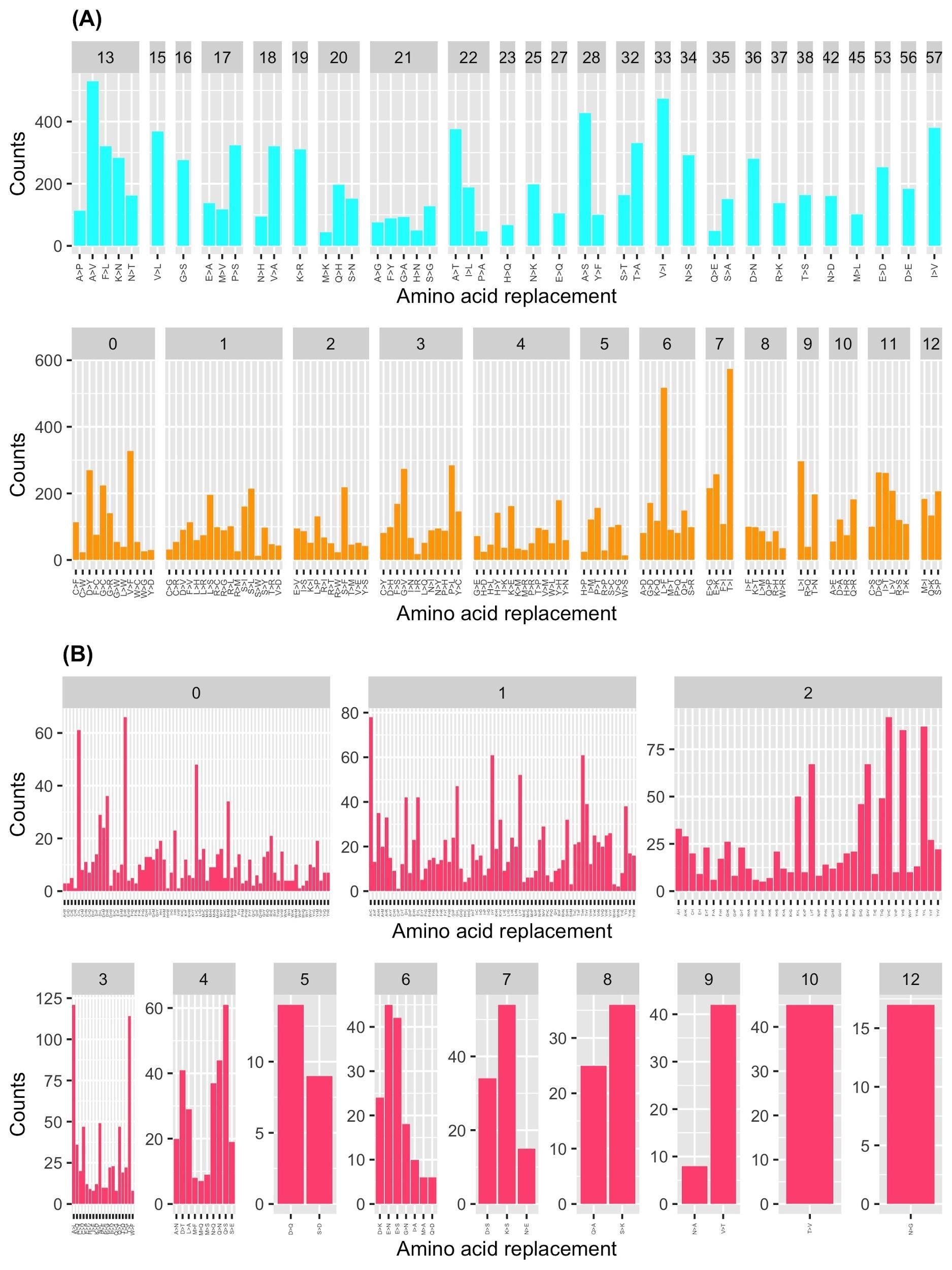
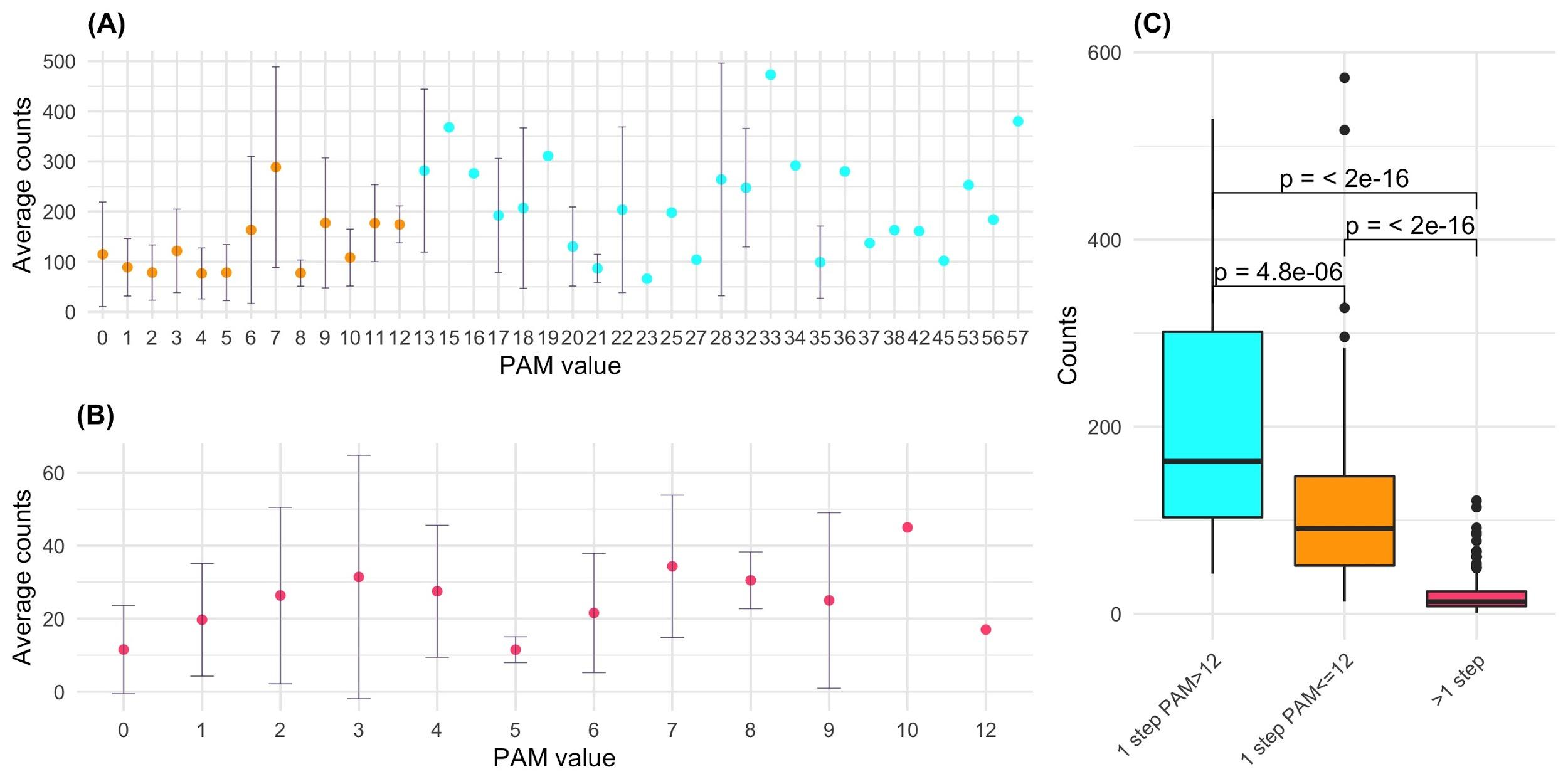
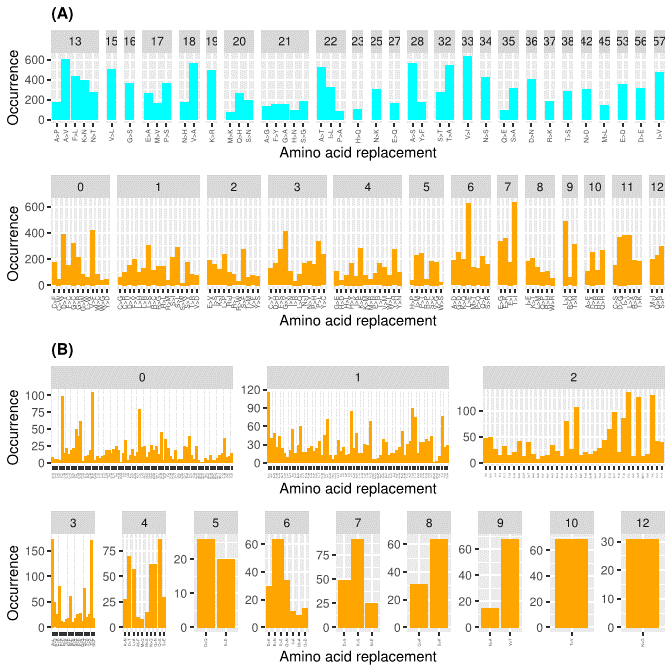
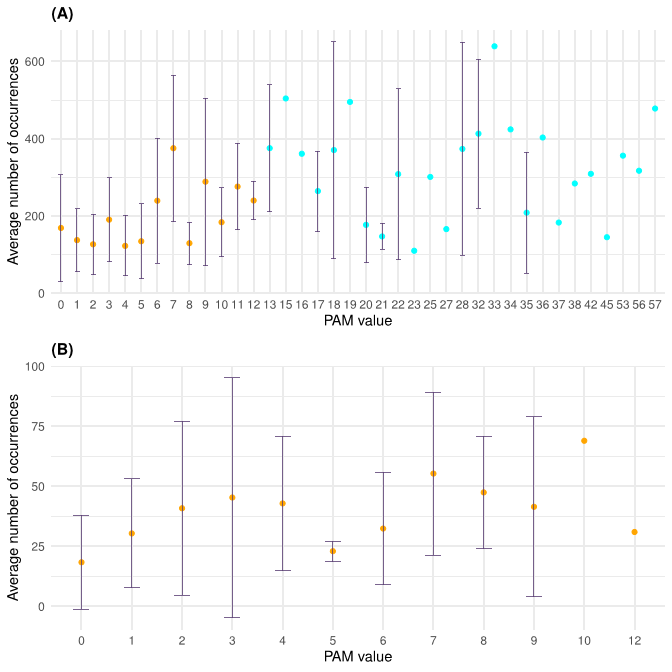
Since the 395 that take place within a single base change correspond to 107 substitutions types, on average each substitution type is found 3.7 times (395/107). The observed substitution types have rather different frequencies. Conservative substitutions present a significantly higher average number of occurrences compared to the non-conservative (Wilcox-test p-value=0.003). When considering average occurrences per PAM bin, we observed that some bins (6, 7, 13, and 17) have very large standard deviations. For these bins, outliers, i.e AA substitutions with enhanced frequencies compared to the others sharing the same PAM value, might be present. The bins of PAM 6, 7, 13, and 17 contain the very frequent substitutions L>F (17 times), T>I (30 times), P>S (19 times), and A>V (21 times), respectively.
Number of mutations 25.634
Almost all possible AA substitutions are observed in DataOct (378 out of 380). The two missing ones (W>D and W>E) are among the most non-conservative substitutions as they require more than one base change and present a PAM value of zero. Mutations that can occur through a single base change present frequencies that are much higher than those requiring multiple base changes.
Conservative mutations are more frequent compared to non-conservative ones. For mutations occurring with a single base change, the quantitative comparison of the frequencies of the conservative and non-conservative mutations using the Wilcox-test provides a p-value of 4.8*10-6. The mutations requiring more than one base change, which are all non-conservative, present significantly lower frequencies compared to the non-conservative mutations occurring in a single base change (Wilcox-test p-value<2*10-16).